Are you worried that masturbation could be causing thin, receding hair? Science suggests there is no truth to this idea. Whether you masturbate often, sometimes, or never will have no effect on your hair one way or another. 
This article will explain how the idea that masturbation can cause health problems first arose. It will examine the arguments that the proponents of this idea usually make, and see what the scientific data and common sense suggests.
While masturbation per se cannot cause hair loss or any other physical disorder, excessive masturbation can have an adverse impact on your personal life.
In particular, the quality of your sexual and romantic relationships can suffer if you masturbate excessively. We will show you how to recognize that this might be the case, and what you can do.
Masturbation is Natural
Masturbation is a very common activity. Nearly all adult men and women have masturbated at some point in their life.
Close to three-quarters of men say they have masturbated within the past year. This number is just over 40% for women (1). As many people are embarrassed to admit they masturbate, the real figures are probably much higher.
Masturbation is also very common from an evolutionary perspective. Humans as a species belong to a small group of primates called The Great Apes. There are four Great Ape species: chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans, and humans. Members of all these species masturbate, both in captivity and in the wild.
Apart from apes, other species of primates include monkeys, lemurs, and lorises. In all, there are over 200 species of primates. In a sample of 65 of these species, scientists observed masturbation in 65% of them. This does not mean that the other 35% never masturbates, but merely that scientists have not yet observed it.
All this suggests that masturbation is deeply rooted in our evolutionary past and non-pathological. It is a behavior we share with our immediate and more extended evolutionary relatives and one that almost all people have engaged in at some point in their lives.
How Did Masturbation Get a Bad Reputation?
People in the West were not very concerned with masturbation up until two or three centuries ago. Then, in the middle 18th century, a Swiss doctor called Samuel Tissot published a book entitled A Treatise on the diseases caused by masturbation.
Many historians regard this book as giving masturbation the bad reputation it carries to this day. In Victorian England, for example, people linked masturbation to anything from blindness and impotence to epilepsy, mental derangement, and even early death.
In the 19th century, the list of symptoms attributed to masturbation was practically endless:
- lethargy
- loss of appetite
- indigestion
- headaches
- vertigo
- lack of sleep
- brain inflammation
- heart palpitations
- loss of weight
- trembling
- paralysis, and more.
Today, no medical professional seriously considers that masturbation – even when excessive – can cause any of these symptoms. 
That doesn’t stop many young men, especially teenagers, from worrying. These are the people most likely to worry that masturbation will cause their hair to fall off, among other things (blindness, hairy palms, etc).
The fact that teenagers are at the same time a) the segment of the population that masturbates the most and b) have the thickest, healthiest hair is a first suggestion that masturbation is harmless.
Let’s see what science actually says.
The Science Behind Masturbation and Hair Loss
No scientific studies have directly examined the relationship between masturbation and hair loss. In other words, no researcher has ever compared the hair of men who masturbate against those who do not. This is because scientists consider this topic so implausible that it is not worth their time.
To settle the matter, we will therefore need to use indirect data. People who claim that masturbation causes hair loss suggest two possible mechanisms:
- Masturbation increases testosterone and consequently DHT levels. Higher DHT levels, in turn, cause hair loss.
- The loss of protein when we ejaculate exacerbates hair loss.
Let’s look at each of these claims in turn.
Does Masturbating Increase DHT?
The most common argument for masturbation and hair loss says that masturbating increases testosterone levels. Some of this excess testosterone is then converted to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
As we will see below, it is true that DHT is linked to hair loss. Blocking DHT in the body is enough to halt hair loss for most men.
However, there is no truth to the claim that masturbation increases testosterone levels. On the contrary, research finds that abstaining from masturbation and ejaculation for 3 weeks leads to an increase in average testosterone levels (2).
Androgen Levels & Hair Loss
it is also important to note that natural variations in testosterone levels are not linked to hair loss.
Scientists have compared the hair of men with high testosterone and DHT levels in their blood to that of men with low levels (within normal limits). The results have been mixed, but most studies don’t find any differences. The consensus is that there is no difference in hair loss between these groups (3).
In other words, even if masturbation did cause a slight increase in testosterone, this would not have any impact on hair loss. It is only unnaturally high levels of testosterone and DHT in the blood that can lead to hair loss. For example, this can happen in men with certain medical conditions or those who abuse anabolic steroids.
Masturbation and Protein Loss
Another way in which masturbation is said to cause hair loss is via loss of protein. According to this view, the protein we lose from ejaculation is the protein that our hair follicles could be using to grow. This leads to protein deficiency and ultimately hair loss.
There is a kernel of truth in this: sperm is indeed rich in protein. However, the quantities of the protein involved are very small. A typical ejaculate is only 3-5ml in volume. Research suggests there is on average 5 grams of protein in every 100ml of sperm (4). This means that you lose at most 0.25 grams of protein every time you ejaculate.
This is a minuscule amount compared to the 50-100 grams of protein which is the daily recommended amount for men (5). To put this into further perspective, you get about 2.5 grams of protein by eating a chicken nugget. This is at least ten times the protein you lose every time you masturbate.
A common-sense objection to the protein theory of masturbation and hair loss is that we also lose the same amount of protein when we ejaculate in sex. Yet nobody suggests that sex can lead to hair loss. This brings us to the next point.
Masturbation, Negative Feelings & Hair Loss Myths
The idea that masturbation causes hair loss is more rooted in psychology than science. 
Females in humans, as in almost all other primate species, are the limiting factor when it comes to sex. In other words, women restrict the frequency of sexual encounters and males have to compete amongst themselves for sexual access to females.
In this competition between men, some will fare better than others. The ones that fare poorly will be left with a surplus of sperm in their testicles. If this sperm can’t be deposited within the vaginal tract of females, it has to leave the body somehow, to make way for fresh sperm.
Masturbation is one way this regeneration process takes place. Meaning that lack of sexual success and masturbation are closely related. This is probably why masturbation can provoke unpleasant feelings like embarrassment and guilt. These negative feelings, in turn, could possibly contribute to some of the masturbation myths, including its link to hair loss.
This view also helps explains some paradoxes. For example, we saw above how there is no evidence that masturbation increases testosterone levels.
On the other hand, researchers have found that men who have multiple sexual partners do indeed have slightly elevated testosterone. This includes men in certain polygamous cultures who are allowed to have more than one wife, as well as men in polyamorous relationships (6).
Yet nobody suggests that having multiple sexual partners can cause hair loss. Unlike masturbation, this situation will not typically provoke negative feelings like embarrassment or low self-esteem.
What Actually Causes Hair Loss?
Hair loss can have many losses. By far the most common type of hair loss, however, is Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA) (7). This accounts for over 95% of hair loss cases in men.
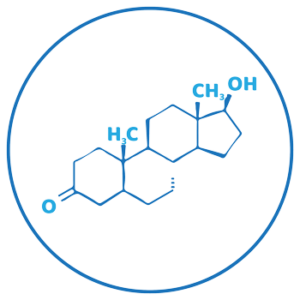
Scientists do not know exactly what causes hair loss. The hormone DHT certainly plays a role. Blocking the production of this hormone with medication like finasteride or dutasteride is enough to halt hair loss for around 85% of men. Around two-thirds will see some regrowth.
The regrowth is typically mild, and these medications cannot restore a full head of hair. This suggests there is more involved than DHT, but scientists are not sure exactly what.
Regardless of the biochemistry involved, the most powerful predictor of AGA is genetics (8). Baldness tends to run in families. If your father, brothers, uncles, and grandparents are bald, you are more likely to go bald yourself. If your male relatives have retained their hair into old age, you are also more likely to do so yourself.
Many men with a genetic predisposition to hair loss often make things worse with poor lifestyle choices or habits. These include:
- Poor hair care routines. The most common of these are shampooing too often, using excessive hair products, or applying harsh chemical and heat treatments.
- Unhealthy diet. Scientists are now reasonably certain of a connection between unhealthy foods, heart disease, and hair loss.
- A sedentary, hectic, stress-filled lifestyle.
Treating Hair Loss
The quicker you start treating your hair loss, the better results you are likely to get. If your baldness advances beyond a certain point, you will not be able to reverse it to any significant degree.
How Hair Loss Progresses
Doctors use the so-called Hamilton-Norwood scale to capture the progression of AGA. A normal head of hair is a 1 on this scale. The first sign of hair loss is typically recession at the temples (2 on the scale).
After this, AGA sufferers progressively lose more and more of the hair at the top of their heads. In very advanced hair loss, they are only left with hair at the back and sides of the head.

If you start treatment for your hair loss while you are still a 2 on the Hamilton-Norwood scale, you might be able to restore a full head of hair. This will not be possible if you are a 3 or 4. If your baldness is very advanced (6 or 7 on the scale) you will hardly see any results.
Here are some of the most common treatment options for hair loss:
Pharmaceutical Treatments
The FDA has approved two treatments for male AGA (9).

Minoxidil is a topical stimulant that can also be used by women with hair loss (10). It stimulates hair follicles to lengthen their growth phase, during which the hair shaft actively grows. The brand name is Rogaine, though you can find many generic versions at a lower cost. The drug is over-the-counter.
Finasteride is a prescription-only oral medication. The brand name is Propecia. Like minoxidil, the patent has now expired, meaning you can find generic versions at a fraction of the price.
Finasteride works by blocking the production of DHT in your body. As mentioned above, just under 90% of men on finasteride will be able to halt their hair loss.
Side effects are the major disadvantage of finasteride. They are sexual and hormonal in nature, including loss of libido, erectile dysfunction, and gynecomastia (11).
An attractive alternative to Propecia pills is applying finasteride topically, directly on your scalp. In combination with minoxidil, topical finasteride will typically give superior regrowth. Because you are not ingesting the drug systemically, the risk of sexual side effects is also very low.
Procuring topical finasteride will require a doctor’s prescription and a compounding pharmacy to prepare the solution. Alternatively, you can order pre-made topical finasteride from online vendors.
Natural Alternatives
If you do not want to take pharmaceutical treatments, there are a number of natural or alternative treatments you can try. Most of these are plant-based natural compounds, which you can use either topically or orally. 
Some of the most common natural treatments for hair loss include saw palmetto, castor oil, essential oils, stinging nettle, and many more.
You can also supplement your diet with the necessary vitamins and minerals your hair follicle need to grow. While these supplements on their own will not typically be enough to reverse your hair loss, they can be a very useful – and healthy – addition to any hair loss regimen.
Devices
In addition to the treatments above, you can also incorporate devices into your hair loss routine.
One of the most popular devices is the dermaroller. This is a very inexpensive handheld tool that can stimulate hair growth by making tiny holes in the skin (12).
You can use it on its own or in combination with a topical stimulant like minoxidil. Learn all about the dermaroller and how to use it in the video below:
Another popular hair loss device is Low-Level Light Therapy (LLLT). These devices typically come as hand-held comes that emit laser light to your scalp. This light stimulates hair growth, though scientists don’t understand how. Regrowth is typically mild at best (13).
Larger LLLT devices come in the form of a helmet. This sits on top of the head and allows you to treat the entire scalp at the same time.
Hair Transplant

Though not a treatment per se, a hair transplant is a surgical procedure that can produce some of the best results of any hair loss intervention (14).
A transplant works by removing healthy hair follicles from the back and side of the head, the so-called donor area. These are then transplanted onto the balding areas at the top and front of the head.
Modern hair transplantation techniques are very advanced, and the results can be very satisfactory. A competent hair transplant surgeon can restore the appearance of a full head of hair, or something very close to that. Like with other interventions, results will be better in cases of mild hair loss.
(check out our complete Hair Transplant guide here).
The main disadvantage of transplants is their very high cost. In the US, this can range from $5,000 for a minor transplant, all the way to $15,000 or $20,000 for extensive procedures.
When to See a Specialist
There are no known side effects to masturbation as such.
However, like most other activities, it is possible to masturbate too much. There is no hard cut-off point for when masturbation becomes excessive. If you are masturbating several times a day and are experiencing any of the following, it might be time to see a specialist (15, 16):
- Reduced sexual desire for your sexual partner (wife or girlfriend)
- Difficulty attaining or maintaining an erection when you are with your partner
- Reduced sensitivity to vaginal intercourse
- Excessive viewing of pornography that is causing you distress

If you suspect your masturbation is causing you problems in any of these areas, you can consult your family or general doctor. They will refer you to a specialized psychologist or psychiatrist. Together you can work on addressing what is causing you to masturbate excessively. You can then develop ways of dealing with the problem and reversing this habit.
Conclusion
Masturbation is a natural and very common human activity. We also share it in common with most other primate species.
As such, there is no reason to think masturbation causes hair loss or any other untoward physical symptom. Accordingly, scientists have not directly studied a possible link between (excessive) masturbation and hair loss.
Those who claim masturbation can cause hair loss typically suggest it causes a) an increase in testosterone and DHT and d) a loss of protein. The available scientific data and common sense do not agree with either of these proposed mechanisms.
While masturbation does not cause hair loss, overdoing it can adversely impact your quality of life. Excessive masturbation, especially in combination with compulsive viewing of pornography, can potentially disrupt your relationships with women.
In some cases, it can also interfere with regular sexual functioning, e.g. difficulty attaining/maintaining an erection and ejaculating.
If you are worried about this, speak to a healthcare professional. There are also various support groups that can help you, either online or in person.
Information contained on this website has not been evaluated by any medical body such as the Food & Drug Administration. All information is for educational purposes only. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease or illness. You must consult a medical professional before acting on any content on this website.


