In this article, you’re going to learn about sunflower oil and its chemical components, some of which contribute in one way or another to hair growth.
Scientific studies show that this seed oil can not only protect your hair and hydrate it, but it can also reverse cellular damage caused by free radicals.
Even further, fatty acids found within sunflower oil have been proven to elongate the hair strand and increase the number of hair follicles.
What more? These fatty acids were shown to be more effective at growing hair than minoxidil!
First, I’ll introduce you to sunflower oil and the various benefits it can provide.
Second, I’ll dive into the scientific research, showing you how sunflower seed oil and its constituents contribute to the treatment of hair loss.
Third, I’ll tell you exactly what you need to know so you can get started using sunflower oil for hair growth now.
What is Sunflower Oil?

The common sunflower, or Helianthus annuus, is a crop, known for its distinct look as well as its edible seeds and oils, which is native to the Americas.
This bright, yellow flower, best grown in moist, well-draining soil and requiring full sun, is a popular crop that is cultivated for its variety of uses, including human consumption, bird and livestock feed, and latex production.
Sunflower oil is obtained from the seed, either through chemical extraction or pressing.
There are three main strains of sunflower seed oil. The standard oil is high in linoleic acid. Due to the numerous health benefits provided by oleic acid, however, two other strains were created with high oleic acid levels and moderate oleic acid levels.
Since there are other oils with naturally high oleic acid levels, if you decide to give sunflower seed oil a try, I would go with standard oil with the highest levels of linoleic acid.
Now, let’s get into the variety of health advantages that sunflower oil supplementation can provide for individuals looking to lengthen and strengthen their hair.
The Benefits of Sunflower Oil for Hair Growth
Rich in Essential Vitamins, Nutrients, and Minerals
High in polyunsaturated fatty acids, and containing rich sources of Vitamins E and K, sunflower seed oil provides your scalp and hair with the nutrients it needs to produce healthy, strong hair strands.
Acts as a Natural Emollient
Similar to jojoba oil, sunflower oil protects against water loss, and in a 2013 study, sunflower seed oil was even shown to improve skin hydration by 12% to 18% in human volunteers.
Targets Free Radicals and Reverses Premature Skin Aging
Sunflower oil is a source high in antioxidants (namely, tocotrienol) which means, that when sunflower seed oil is supplemented, free radical activity is kept at bay, and damage previously caused by free radicals (such as hair thinning and loss) is reversed.
Promotes Repair of Damaged Skin
Alongside its moisturizing properties, sunflower oil has also been proven to accelerate the repair of the damaged skin barrier.
Darmstadt et al found, in the epidermal layer of mice, sunflower oil accelerated skin barrier recovery within one hour of application, and this effect was sustained even five hours after application.
To better understand the above-listed benefits of sunflower seed oil, let’s take a look at the research.
Sunflower Oil’s High Linoleic Acid Content: An Array of Hair Growth Benefits
In previous articles, I’ve discussed the positive impact that both oleic and linoleic acids have on hair growth. In these other articles, however, oleic acid seems to be the main focus, as it’s a major component of olive oil and canola oil.
Today, however, I’d like to focus on linoleic acid and what it can do for the good of your hair.
What is Linoleic Acid?
Linoleic acid is an omega-6 fatty acid. Omega-6 fatty acids are vital to human health, as they maintain bone health, regulate the metabolism, support the reproductive system, and even stimulate the growth of skin and hair.

As a polyunsaturated fat, linoleic acid contributes significantly to cardiovascular health and is also high in Vitamin E, a vital nutrient that I’ll discuss in further detail later.
In addition to the health advantages provided by linoleic acid, the metabolism of this omega-6 fatty acid within the body converts it into various other fatty acids, all of which have their roles to play.
Arachidonic acid plays a huge role in hair growth stimulation, which I’ll be sure to highlight later.

Sunflower Oil’s Linoleic Acid: A Treatment for Scarring Alopecia

While male-pattern baldness tends to be one of the better-known forms of alopecia, other types do exist.
One such type is scarring alopecia, which is characterized by plaque-like skin lesions that damage the hair follicles and cause hair fall.
The healing abilities of linoleic acid, however, are something to be noted.
In 2004, scientists tested these abilities on lambs.
The lambs were split into two groups, one group treated with the application of sunflower seed oil and the other group treated with Vaseline (control).
At the 7- and 21-day marks, it was obvious that the lambs treated with sunflower seed oil saw much better healing, both in terms of reduced wound size and increased rate of wound contraction.
By the 21st day, treated wounds showed complete resurfacing of the epithelium, including hair follicles.
While still untested on humans with scarring alopecia, the results of this study do provide promise.
First, this study shows that sunflower oil is a direct healer of wounds.
Second, and perhaps most important for those with scarring alopecia, the application of sunflower seed oil may even lead to the regrowth of hair follicles in previously scarred areas.
Arachidonic Acid: A Metabolite of Linoleic Acid and Inducer of Hair Growth
I mentioned above that linoleic acid synthesizes into other fatty acids. One such fatty acid, arachidonic acid, arachidonic acid, was shown to induce hair growth in  mice in a 2016 study performed by Munkhbayar et al.
mice in a 2016 study performed by Munkhbayar et al.
In the particular part of the study which focused on hair growth in mice, the dorsal region of female mice was shaved, and the hair follicles were confirmed to be entering the anagen phase.
The mice were split into three groups and received an applied mixture of either a) a placebo; b) arachidonic acid; or c) minoxidil. This treatment took place over four weeks.
At the end of the 28-day study, it was seen that mice receiving the applied mixture of arachidonic acid grew longer hair in a faster amount of time than those in either the control or minoxidil groups.
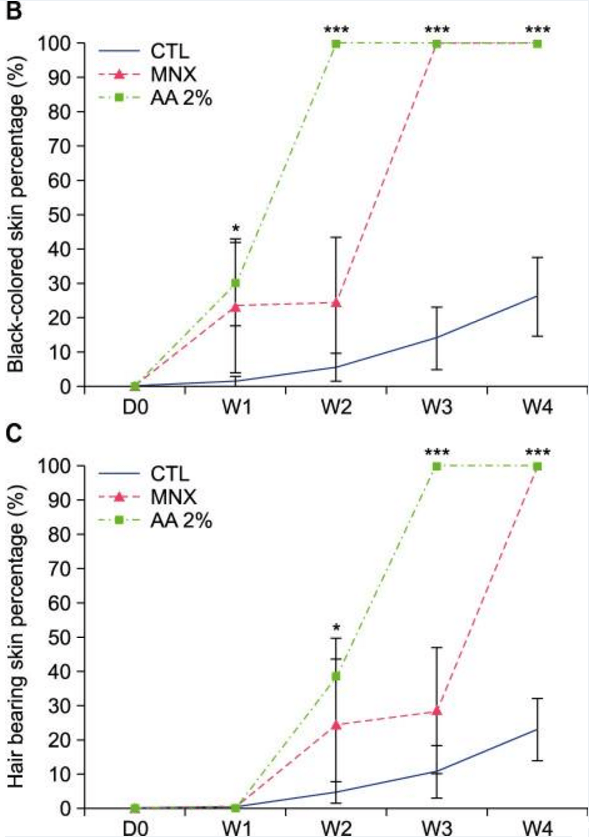
In another part of the study, researchers were looking at the effect arachidonic acid had on the elongation of the human hair shaft and the proliferation of dermal papilla cells.
Using hair shaft samples collected from healthy males between the ages of 20 and 50, researchers cultured the samples for 12 days, eventually adding varying concentrations of arachidonic acid (AA) to determine its effects.

Researchers found hair shaft growth at AA concentrations of 1 µM, 2 µM, and 5µM.
The growth seen was higher than that of the control group. Further, the scientists wanted to see if AA played a role in follicular cell proliferation, and they used a known proliferation marker, Ki-67, to do so.
With the use of immunofluorescence staining, scientists saw that concentrations of AA from 1 µM to 5 µM caused an increase in Ki-67 found along the follicular matrix, leading to significant proliferation of cells over the control group.
This research study provides scientists with two essential pieces of information.
The first piece is in regards to arachidonic acid’s hair growth abilities. As was shown in the application of AA to the dorsal regions of mice, arachidonic acid was more effective at growing hair than even minoxidil.
The second piece of information shows the concentration levels at which arachidonic acid is shown to be most beneficial.
As too much arachidonic acid can induce inflammation, negatively impacting the growth of hair and the production of new hair follicles, high levels of AA are to be avoided in treatment.
In this particular study, the concentrations of 2 µM and 5 µM seem to be the most effective, while 10 µM is shown to reverse the positive effects.
Vitamin E in Sunflower Oil: A Potent Antioxidant
Free radicals are the culprit in several age-related processes, such as hair greying, wrinkles, and hair thinning and loss.
Through the destruction of vital cells, as well as the targeting of important molecules such as proteins and lipids, free radicals lead to the breaking down and interruption of necessary processes.

Now, as a result of this damage, the body (and particularly the scalp) responds by producing inflammation as a way to fight the attack.
Unfortunately, chronic inflammation can be just as destructive, if not more, than free radicals.
And, while inflammation may be a temporary fix for free radical damage and cell destruction, it cannot properly handle the threat.
So, what can be done?
This is where antioxidants come in.
Antioxidants are the free radical fighting heroes of the body, donating a part of themselves to ensure that free radicals don’t go looking elsewhere (like, to the molecules within our body) for their needs.
There are hundreds, possibly even thousands, of different antioxidants. Sunflower oil has one particular antioxidant, however, and that’s Vitamin E.

Vitamin E works by interrupting the process of lipid peroxidation.
This occurs when free radicals target the lipid molecules within the body, leading to the destruction of these vital molecules and ultimately causing tissue damage.
To understand the role that Vitamin E plays in preventing hair loss, let’s take a closer look at a 2010 Malaysian study.
For eight months, researchers tracked the effects of tocotrienol (a member of the Vitamin E family) on male and female volunteers suffering from varying levels of alopecia.
Out of the 38 total participants, 17 received a placebo while 21 received an oral dose of 100 mg of mixed tocotrienols. All participants took their oral supplements once per day.
Throughout the study, Beoy et al. counted the amount of hairs found within a predetermined area of scalp, as well as collected hair clippings to collect weight data.

Unfortunately, tocotrienol did not have a significant effect on hair weight.
What did the researchers believe was responsible for these results?
Well, while the researchers do know that Vitamin E’s antioxidants play a significant role in the results seen, Vitamin E supplementation may also increase the size of blood vessels.
This means that hair follicles will see an increase in nutrients, as well as an increase in the amount of harmful waste that is removed from the scalp.
How to Use Sunflower Oil for the Treatment of Hair Loss

Supplementation of sunflower oil can either be done through oral consumption, for example eating the seeds or direct application. However, while increasing your oral consumption of sunflower seed oil may provide you with a few general health benefits, direct application to the scalp and hair appears to be the most efficient method of supplementation.
So, how can you add sunflower oil to your usual hair care routine?
Increase Dietary Intake
The light taste of sunflower oil makes it an excellent addition to your favorite recipes.
Add it to your salads and soups for an extra dose of healthy fats and Vitamin E, or use it to stir fry your favorite vegetables. If you’re in a hurry, eat sunflower seeds as a snack.
Add It To Your Hair Care Products

Sunflower seed oil makes an excellent carrier oil for a variety of homemade hair care products.
If you’d like to give sunflower oil a try, then take a look at the Rosemary Oil & Zesty Lemon conditioner below.
Ingredients:
- Apple cider vinegar (1 cup)
- Rosemary oil (10 drops)
- Lemon juice (2-3 tablespoons)
- Sunflower oil (1/3 cup)
Directions:
Mix the above four ingredients until thoroughly combined. After washing your hair, apply the conditioner to your wet scalp and hair, allowing it to soak in for 5 minutes. After absorbing all the nutrients, rinse thoroughly in lukewarm water.
Hair Benefits:
The apple cider vinegar acts as a gentle cleanser, removing any left behind shampoo residue and naturally cleansing your hair strands and scalp.
Lemon juice, doubly beneficial in this recipe, provides both a boost of Vitamin C and a shock of antioxidants. The rosemary oil adds a soothing effect, while simultaneously dilating the blood vessels to ensure proper nutrient delivery to the hair follicles.
Side Effects of Sunflower Oil Supplementation
For the majority of healthy individuals looking to supplement with sunflower oil, the side effects are few.
For dermal application, these side effects may include mild irritation or allergic reaction.
This is why it’s a good idea to test any supplements on the inside of your wrist before applying to the scalp. If no reaction after 24 hours you should be okay to try using it. Discontinue use if irritation starts. In moderation, those who consume sunflower oil should stick to a consumption of between 25% to 35% of their daily recommended calorie intake.
If you suffer from chronic medical conditions, such as high cholesterol or heart disease, speak with your physician before supplementation.
Women who are pregnant or nursing are likely safe to supplement with sunflower oil, both dermally and orally, however, your physician can provide you with the best advice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sunflower oil can provide your hair and scalp with a variety of benefits that may contribute to accelerated hair growth and strengthening of the hair strands.
Shown to be more effective at growing hair in mice than minoxidil, those who are looking for an all-natural alternative to the popular over-the-counter medication may find sunflower seed oil to be an appropriate substitute.
I do believe, however, that there are more effective methods of treating hair loss, but sunflower oil might be an option for people who are unable to use other more effective methods.
Information contained on this website has not been evaluated by any medical body such as the Food & Drug Administration. All information is for educational purposes only. We do not aim to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease or illness. You must consult a medical professional before acting on any content on this website.


